Written by Aralia Blackman

Perspective: If we assume that the ages that are most vulnerable to negative emotions are girls 10 – 14 and boys 12 – 16, how does social media/gaming as well as violent music hamper their development?
Introduction
Adolescence is a crucial period for emotional and psychological development. It is during this time that young people form their identities, develop emotional resilience, and learn to navigate social relationships. Assuming that girls aged 10-14 and boys aged 12-16 are particularly vulnerable to negative emotions due to hormonal changes, peer pressure, and self-esteem fluctuations. The rise of digital technology, including social media, gaming, and music streaming, has introduced new challenges that impact adolescent mental health. This article explores how these forms of media contribute to increased anxiety and depression, reduced emotional regulation, impaired social skills, heightened aggression, and declining cognitive development, while also discussing potential solutions to mitigate these negative effects.
1. Increased Anxiety and Depression
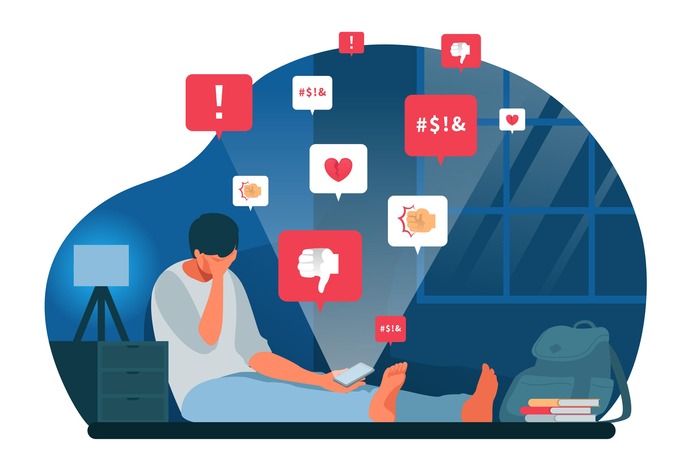
Social media platforms such as Instagram, TikTok, and Snapchat play a significant role in shaping self-perception. Young girls, in particular, are exposed to unrealistic beauty standards through edited photos and influencer culture, leading to body dissatisfaction and low self-esteem. The constant comparison to peers and celebrities fosters feelings of inadequacy and anxiety. Additionally, cyberbullying is a widespread problem, with many adolescents experiencing harassment, exclusion, or negative comments, further increasing stress and depressive symptoms.
Excessive gaming, particularly among boys, has been linked to social withdrawal and increased irritability. Many adolescents spend hours playing multiplayer online games, prioritizing virtual interactions over real-life relationships. This can lead to gaming addiction, decreased motivation for schoolwork, and difficulty managing real-world stressors. Some studies also suggest that prolonged exposure to violent video games may increase aggressive thoughts and behaviors, contributing to emotional instability.
Music, particularly violent or explicit genres such as rap and heavy metal, can also influence adolescent emotions. Lyrics that glorify aggression, substance abuse, or toxic relationships can normalize destructive behavior and reinforce negative emotions. Studies have found that exposure to violent music lyrics can heighten aggressive thoughts and desensitize listeners to real-world violence.
Solution: Media literacy education can help adolescents critically analyze the content they consume and develop resilience against harmful influences. Schools should incorporate lessons on identifying unrealistic portrayals in social media and understanding the effects of violent content. Parents can also encourage open discussions about online experiences to help their children navigate digital spaces more safely.
2. Reduced Emotional Regulation
The digital world often presents a distorted version of reality, making it harder for young people to develop healthy emotional regulation skills. Constant exposure to carefully curated online personas can lead to unrealistic expectations about life and relationships. Many teens struggle with processing disappointment or failure because they are conditioned to see only success and perfection on social media.
Gaming, particularly competitive or violent games, can contribute to impulsive behavior. The adrenaline rush from high-stakes gameplay often results in frustration, anger, or hostility when things do not go as expected. This can translate into real-world emotional outbursts and difficulty managing stress in everyday situations.
Music can also shape emotional responses. Aggressive lyrics or themes of hopelessness and self-destruction may reinforce feelings of anger or sadness in vulnerable teens. For example, research has shown that repeated exposure to music that emphasizes revenge or retaliation can make listeners more likely to adopt hostile worldviews.
Solution: Parental involvement plays a key role in helping adolescents develop emotional regulation. Parents can guide children in managing their screen time, discussing the emotional impact of media, and modeling healthy emotional expression. Encouraging teens to engage in mindfulness exercises and offline activities such as sports, art, and reading can also support emotional stability.
3. Hindered Social Skills and Communication
The rise of digital communication has altered the way adolescents interact with others. Heavy social media and gaming use often replace face-to-face interactions, making it harder for teens to develop strong interpersonal skills. Many young people struggle with in-person conversations, emotional expression, and conflict resolution due to their reliance on texting and online messaging.
In gaming communities, social interactions are often centered on competition rather than collaboration, which can lead to difficulties in real-world teamwork. Online anonymity can also encourage toxic behavior, reducing empathy and reinforcing aggressive communication styles.
Violent music lyrics, particularly those that normalize disrespect or hostility, can shape attitudes toward relationships. Teens who frequently listen to songs that degrade others or promote dominance may struggle to form healthy, respectful connections with peers, romantic partners, or authority figures.
Solution: Schools and families can promote in-person social interactions through group activities, team sports, and community service programs. Encouraging adolescents to participate in extracurricular activities that involve collaboration can strengthen their interpersonal skills. Additionally, limiting online interactions and fostering open discussions about respectful communication can improve social development.
4. Increased Aggression and Desensitization
Exposure to aggressive content in social media, gaming, and music can desensitize young minds to violence. Many online platforms, such as Twitter and Reddit, feature viral content that includes fights, pranks, or bullying, normalizing harmful behavior. When adolescents frequently witness or engage in these toxic online environments, they may become less sensitive to the consequences of aggression.
Violent video games have been shown to increase aggressive tendencies in some individuals. A meta-analysis found that players who frequently engage in violent gaming scenarios exhibit heightened aggressive cognition and reduced empathy toward others.
Similarly, repeated exposure to music with violent themes can alter perceptions of aggression. Studies have indicated that teens who listen to music with hostile lyrics are more likely to justify aggression in real-life situations, seeing it as a normal or necessary response to conflict.
Solution: Implementing stricter regulations on violent content and promoting digital well- being programs can help address aggression and desensitization. Social media platforms and gaming developers can introduce content filters and parental controls to limit exposure to violent material. Schools can also incorporate media literacy programs to help students critically evaluate aggressive content and its potential impact on behavior.
5. Impaired Cognitive Development and Academic Performance
Excessive engagement with social media and gaming can negatively affect cognitive development and academic performance. Screen addiction often leads to sleep deprivation, as many teens stay up late scrolling through social media or playing video games. Sleep deprivation is linked to reduced concentration, memory impairment, and lower academic achievement.
Additionally, the rapid, fast-paced nature of digital content consumption shortens attention spans. Many adolescents struggle to focus on tasks that require sustained mental effort, such as reading or problem-solving, because they are accustomed to instant gratification from short-form content like TikTok videos or fast-paced gaming sequences.
Certain music genres, particularly those emphasizing materialism, rebellion, or substance abuse, can also impact academic motivation. Teens who strongly identify with music that glorifies skipping school or engaging in reckless behavior may be less inclined to prioritize their education.
Solution: Schools and parents can encourage balanced screen time and promote a structured daily routine that includes sufficient sleep, academic focus, and recreational activities. Educators can also introduce interactive and engaging learning methods to capture students’ attention and minimize distractions caused by digital media. Encouraging music consumption that inspires creativity and motivation rather than negativity can further enhance cognitive development.
By implementing these solutions, society can better support adolescents in developing healthier emotional regulation, improved social skills, and a more balanced relationship with digital media.
Conclusion
Adolescents, particularly girls aged 10–14 and boys aged 12–16, are at a critical stage of emotional and psychological development. During this period, they are highly susceptible to negative emotions due to hormonal changes, social pressures, and evolving self-identity. Social media, gaming, and violent music significantly hamper their development by intensifying these vulnerabilities.
Social media exposes young girls to unrealistic beauty standards and constant peer comparison, leading to heightened anxiety, low self-esteem, and even depression. The pressure to conform to curated online personas fosters insecurities and a distorted sense of self-worth. Similarly, boys immersed in gaming, especially violent or competitive games, are prone to social withdrawal, irritability, and impulsive behavior, which can hinder their ability to regulate emotions and manage real-world challenges.
Violent music, whether through aggressive lyrics or themes of rebellion and hostility, normalizes destructive behavior and reinforces negative emotional states. This can shape adolescents’ worldviews, making them more prone to adopting hostile attitudes or justifying aggression. Moreover, the habitual consumption of such content can desensitize them to violence and impair their social skills, as they struggle to build empathy and maintain healthy interpersonal relationships.
As a result, these digital influences can severely disrupt the development of emotional regulation, social competence, and cognitive growth. Addressing this issue requires a balanced approach that includes media literacy education, parental guidance, and the promotion of positive media engagement to support healthy emotional and social development.
References
Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2018). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents. Preventive Medicine Reports.
Anderson, C. A., Carnagey, N. L., & Eubanks, J. (2003). Exposure to violent media: The effects of songs with violent lyrics on aggressive thoughts and feelings. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology.
Anderson, C. A., & Bushman, B. J. (2001). Effects of violent video games on aggressive behavior, aggressive cognition, aggressive affect, physiological arousal, and prosocial behavior: A meta-analytic review. Psychological Science.
Abad-Santos, A. (2023, March 14). What are kids watching on tablets? Parents. Retrieved from https://www.parents.com/what-are-kids-watching-on-tablets- 11689876
Carlisle, M. (2023, April 5). American Psychological Association releases teen video viewing guidance. TIME. Retrieved from https://time.com/7177874/teen-video- viewing-guidance-apa/